Spine Surgeon
Radiculopathy
Radiculopathy
Radiculopathy refers to a condition characterized by irritation, compression, or inflammation of one or more spinal nerve roots, typically as they exit the spinal column. This can occur in various regions of the spine, including the cervical (neck), thoracic (upper back), or lumbar (lower back) areas. The compression of nerve roots can result from conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, degenerative disc disease, or foraminal stenosis.
What are the types of Radiculopathy?
- Cervical Radiculopathy: Affecting nerves in the neck, cervical radiculopathy leads to pain, weakness, and numbness in the shoulders, arms, and hands. Compression of a nerve as it exits the spinal cord is the primary cause.
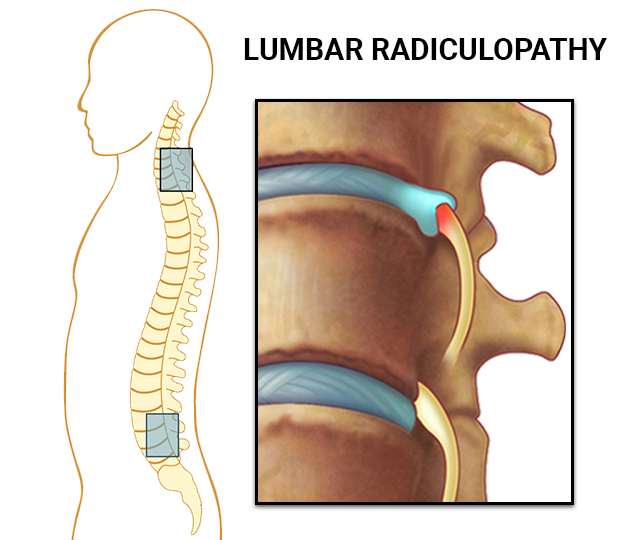
- Lumbar Radiculopathy: This type impacts nerves in the lower back, causing pain, weakness, and numbness in the legs and feet. Lumbar radiculopathy is often associated with sciatica pain.
- Thoracic Radiculopathy: Targeting nerves in the middle back, thoracic radiculopathy results in pain, weakness, and numbness in the chest and abdominal area.
What are the causes and symptoms of Radiculopathy?
Causes
- Disc Herniation: Displacement or bulging of spinal discs that may compress nerve roots.
- Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal, leading to pressure on nerves.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Wear and tear on spinal discs over time, contributing to nerve compression.
- Bone Spurs: Abnormal bony growths that can impinge on nerve roots.
- Inflammation: Swelling or inflammation of surrounding tissues affecting nerve function.
Symptoms
- Radiating Pain: Sharp or shooting pain that follows the path of the affected nerve.
- Weakness: Reduced strength in muscles connected to the affected nerve.
- Numbness: Loss of sensation or tingling in areas served by the affected nerve.
- Tingling or “Pins and Needles”: Sensations of prickling or tingling in the extremities.
- Muscle Atrophy: Gradual wasting or weakening of muscles due to nerve dysfunction.
How to diagnose radiculopathy?
Clinical Assessment of Symptoms: Detailed evaluation of the nature and progression of symptoms, including pain, weakness, and sensory changes.
Neurological Examination: Evaluation of nerve function, reflexes, and sensory responses to identify signs of nerve compression.
Imaging Studies:
- X-rays: To visualize bony structures and identify any abnormalities or misalignments.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of soft tissues, including the spinal cord and nerve roots.
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: Useful for detecting bony abnormalities, such as herniated discs or bone spurs.
Electrodiagnostic Tests:
- Electromyography (EMG): Measures electrical activity in muscles to assess nerve function and detect abnormalities.
- Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS): Measures the speed of electrical impulses through nerves, helping identify areas of nerve compression.
Selective Nerve Root Block: Injection of a local anesthetic and corticosteroid into specific nerve roots to determine if symptoms are relieved, aiding in pinpointing the affected nerve.
Myelogram: Injection of contrast dye into the spinal fluid followed by X-rays or CT scans to visualize the spinal cord and nerve roots.
Blood Tests: May be conducted to rule out systemic conditions that could contribute to nerve compression.
What is the treatment for radiculopathy?
Medication/Ice/Heat:
Prescription anti-inflammatory drugs or muscle relaxants may be recommended to ease nerve irritation. Applying ice or heat can also be part of the treatment plan.
Physical Therapy/Specific Exercises:
Tailored exercises aim to improve range of motion and strengthen muscles around the affected nerve. Ice or heat applications may be suggested.
Epidural Steroid Injection:
To alleviate nerve pain in the back or leg, an epidural steroid injection may be administered. The medication is delivered around the nerve in the epidural space.
Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS):
For severe, unresponsive pain, Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS) may be considered. This implantable device, controlled by a remote, interrupts nerve signals before reaching the brain, providing relief from pain caused by a pinched or injured nerve. A trial period is typically conducted before permanent implantation to assess treatment effectiveness.
What are the surgical treatments for radiculopathy?
- Microdiscectomy
- Laminectomy
- Foraminotomy
- Discectomy
- Spinal Fusion
- Artificial Disc Replacement
- Endoscopic Surgery
- Nucleoplasty
- Intradiscal Electrothermal Therapy (IDET)
- Peripheral Nerve Surgery
For specialized care in managing radiculopathy, book your appointment with Synapse Spine in Mumbai today. Take the first step towards personalized treatment and optimal spinal health.