Spine Surgeon
neck pain specialist Mumbai
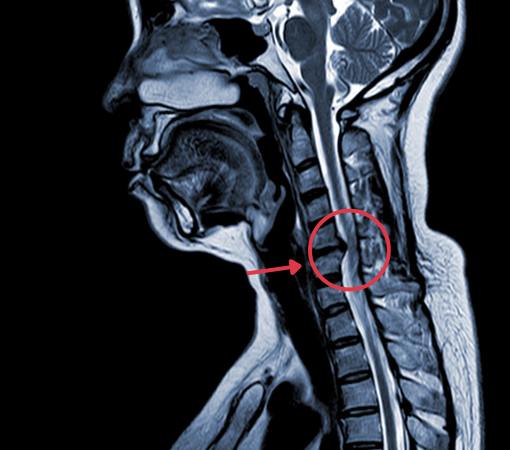
Cervical myelopathy
Cervical myelopathy is a condition characterized by spinal cord compression within the cervical region, specifically between the C1 and T1 vertebrae. This syndrome can present symptoms similar to other neurological and degenerative disorders, posing a challenge for accurate diagnosis. Treatment focuses on surgically decompressing the spinal canal, which may involve anterior, posterior, or a combined approach based on the compression’s location and specific patient-related factors. Early treatment, before the progression of severe symptoms, generally results in favorable outcomes.
What are the causes and symptoms of Cervical Myelopathy?
Causes of Cervical Myelopathy
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Age-related wear and tear on the spinal discs can lead to cervical myelopathy.
- Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal in the cervical region compresses the spinal cord.
- Herniated Discs: Discs that bulge or rupture can press against the spinal cord.
- Osteophytes: Bone spurs that grow as a result of spinal osteoarthritis can impinge on the spinal cord.
- Trauma: Accidents or injuries causing fractures or dislocations of the vertebrae can compress the spinal cord.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Inflammation of the cervical spine joints can lead to spinal cord compression.
Symptoms of Cervical Myelopathy
- Neck Pain and Stiffness: Often one of the first symptoms, reflecting the compression in the cervical spine.
- Numbness and Tingling: These sensations can occur in the arms, hands, legs, or feet, indicating nerve compression.
- Weakness: Muscle weakness in the limbs can make daily tasks difficult.
Coordination Problems: Difficulty with fine motor skills and changes in walking gait can manifest. - Balance Issues: Individuals may experience problems with balance, increasing the risk of falls.
- Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction: In severe cases, control over bladder or bowel movements may be lost.
How to diagnose cervical myelopathy?
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of soft tissues, including the spinal cord and nerves, to identify areas of compression.
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scan: Offers a detailed view of the spinal column and can help identify bone spurs, herniated discs, or other causes of spinal cord compression.
- X-rays: Can reveal the overall structure of the spine and indicate degenerative changes or alignment issues.
- Myelogram: Involves injecting a contrast dye followed by X-ray or CT imaging to provide detailed views of the spinal canal and nerve roots.
- Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies: These tests measure the electrical activity of muscles and the speed of nerve signals, respectively, to detect nerve damage.
What is the treatment option for cervical myelopathy?
- Physical Therapy: Aimed at strengthening neck muscles, improving flexibility, and reducing pain. It can also help with balance and coordination.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce swelling and pain. In some cases, muscle relaxants may be prescribed to ease muscle spasms.
- Cervical Collar: A neck brace can be used temporarily to provide support, limit movement, and allow the neck to heal.
- Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms and learning safer ways to perform daily tasks.
What are the surgical options for Cervical Myelopathy?
- Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF)
- Cervical Laminectomy
- Laminoplasty
- Posterior Cervical Fusion
- Cervical Disc Replacement
Synapse Spine is your dedicated partner in addressing Cervical Myelopathy Best neck pain specialist Mumbai, India , offering tailored treatment options for your unique needs. With a focus on minimally invasive surgery techniques, we strive to provide effective solutions with improved recovery times. Schedule your appointment today to begin your journey towards recovery with Synapse Spine.