Spine Surgeon
Disc Replacement surgery in Mumbai
Disc replacement surgery
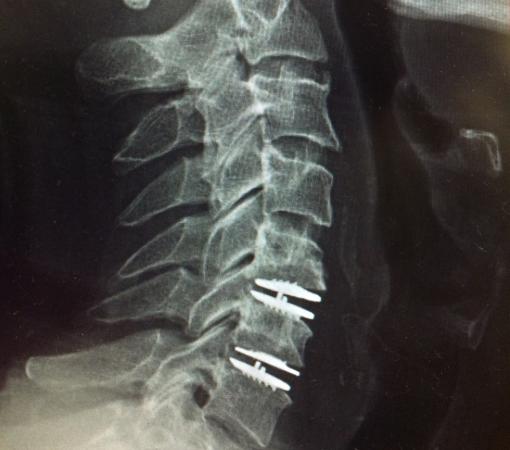
Disc replacement surgery in mumbai involves the placement of a “mobile” device into the intervertebral disc space following discectomy. Unlike spinal fusion surgery, which eliminates movement, this procedure aims to preserve motion at the operated level. The loss of movement in fusion surgery can result in reduced spinal flexibility and potentially increase stress on adjacent spine levels, leading to accelerated degeneration (Adjacent Segment Degeneration/ASD). ASD is a significant factor contributing to the need for revision spine surgeries, particularly in cases involving multi-level fusions. Artificial disc replacement offers a solution to these issues by avoiding the drawbacks associated with spinal fusion.
What are the types of disc replacement surgery?
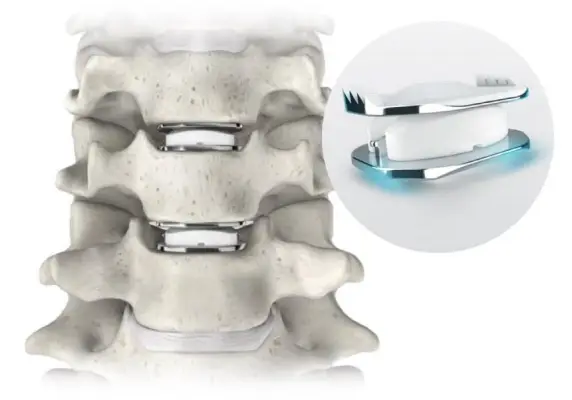
- Total disc replacement: This procedure involves the removal of the damaged or diseased disc tissue, followed by the implantation of a device into the space between the vertebrae.
- Disc nucleus replacement: With disc nucleus replacement, only the center of the disc (known as the nucleus) is removed and replaced with an implant. The outer part of the disc remains intact and is not removed during the procedure.
What are the indications of disc replacement surgery?
- Spondylosis: Disc replacement can effectively address mild to moderate spondylosis, providing relief from degenerative disc pain while maintaining spinal motion.
- Cervical Disc Prolapse: Ideal for younger patients with cervical disc herniation, disc replacement surgery can alleviate symptoms and restore functionality.
- Multilevel Cervical Instrumentation Surgery: In cases of multilevel cervical disc disease requiring instrumentation surgery, disc replacement can be incorporated to preserve spinal mobility. By replacing discs at both ends while fusing middle levels, this approach minimizes stress on adjacent segments, reducing the risk of Adjacent Segment Degeneration (ASD).
What materials are artificial discs composed of?
Artificial discs are typically crafted from metal or biopolymer materials, such as hydrogel, which expands as it absorbs water, or a combination of both. The prevalent complete disc replacement designs usually feature two plates: one affixed to the vertebrae above the replaced disc and the other to the vertebrae below it. Advanced devices may include a soft, compressible plastic-like component positioned between these plates. These devices facilitate bone movement through smooth, often curved, surfaces that glide across each other.
How long does it take to recover from disc replacement surgery?
After surgery, most people spend one to two nights in the hospital, maybe more if they have extra pain or problems. Patients typically experience a speedy recovery, being able to walk and leave bed within just a few days. Some may wear a brace for support. Physical therapy helps with recovery, including exercises and walking. Regular checkups and X-rays ensure the disc stays in place. Patients should avoid heavy lifting for about four weeks and return to work after being consulted by their spine surgeon.
What are the benefits of disc replacement surgery?
- Preservation of Spinal Flexibility- Disc replacement maintains spinal mobility, unlike fusion surgery, enhancing natural movement and reducing strain on adjacent segments.
- Alleviation of Pain Symptoms- Symptoms are relieved without restricting movement, enabling patients to bend and twist freely after surgery.
- Elimination of Bone Graft Need- Artificial Discs negate the requirement for bone grafts, streamlining surgery and potentially hastening recovery compared to fusion procedures.
Consider Disc replacement surgery in mumbai as an alternative to traditional spinal fusion at Synapse Spine Mumbai. Our experienced spine surgeons offer this innovative procedure to replace damaged discs, restoring mobility and reducing pain. Schedule your consultation to explore whether disc replacement surgery is right for you.